
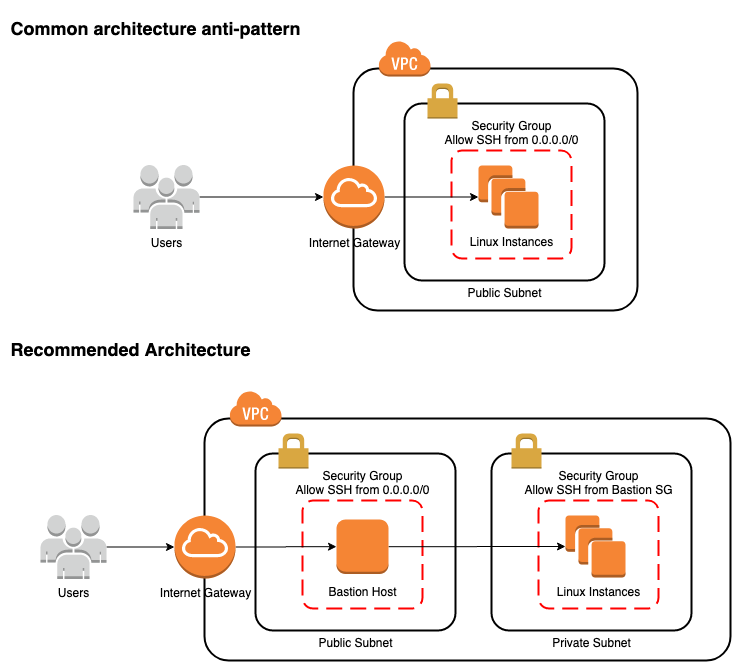
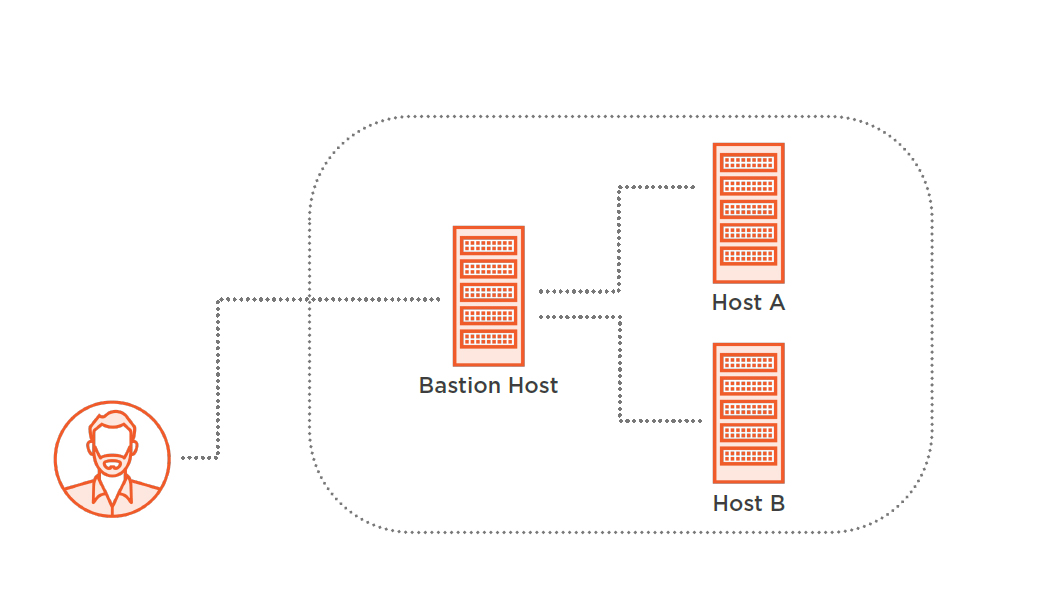
Make sure to use the hostname 127.0.0.1 when accessing a MySQL DB instance. Note: MySQL tries to connect using the socket if you use the keyword localhost when connecting to DB instance. $ psql -hlocalhost -Upostgres -p -d postgres Template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres + Template0 | rdsadmin | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/rdsadmin + Rdsadmin | rdsadmin | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | rdsadmin=CTc/rdsadmin Postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges The solution sets up a Multi-AZ environment and deploys Linux. The bastion hosts provide secure access to Linux instances located in the private and public subnets of your virtual private cloud (VPC). SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.2, cipher: ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, bits: 256, compression: off) This AWS Solution adds Linux bastion hosts to your new or existing Amazon Web Services (AWS) infrastructure for your Linux-based deployments. p = 'local-port-you-connect-to' from the SSH Tunneling commandĪ483e73d651f.ssh rahul_saha$ psql -hlocalhost -Upostgres -p5432 -d postgres U = the username present in the DB for connectivity Psql -hlocalhost -Upostgres -p -d postgres The following example connects to PostgreSQL, but you can also use this method to connect to MySQL, or any other engine you want to connect to. Now that SSH tunneling is in place, you can connect to your DB instance from your local Linux/macOS machine. debug1: Local forwarding listening on ::1 port 5432.debug1: Local forwarding listening on 127.0.0.1 port 5432.debug1: Local connections to LOCALHOST: 5432 forwarded to remote address 172.31.39.62:5432.When you run the command above (SSH tunneling), you configure the following settings: Run the following command from your Linux/macOS machine to create a tunnel for connectivity from your machine: Syntax 1: Set the security group to allow the IP of the Linux/macOS machine you are trying to connect from.ģ. Set your Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance to be accessible from internet, with public subnets (i.e., has Internet gateway - igw in route tables). Launch the smallest available EC2 instance in the same VPC as your DB instance. Set the security group to allow the DB to port ( 5432, 3306) from all IPs.Ģ. Set the publicly accessible parameter to no, with private subnets (i.e., no Internet gateway - igw in route tables). Set your Amazon RDS DB instance to private by modifying the DB instance.
#Aws bastion host vs nat instance how to#
This example shows you how to set up a bastion host to connect to your RDS DB instance from a Linux/macOS machine, even though the RDS DB instance is private. You can also use this method to connect to Aurora Serverless and RDS Proxy from outside the VPC. If you cannot use either a VPN or AWS Direct Connect, then the preferred option is to use a bastion host. To connect to a private Amazon RDS or Amazon Aurora DB instance, it's a best practice to use a VPN or AWS Direct Connect.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
